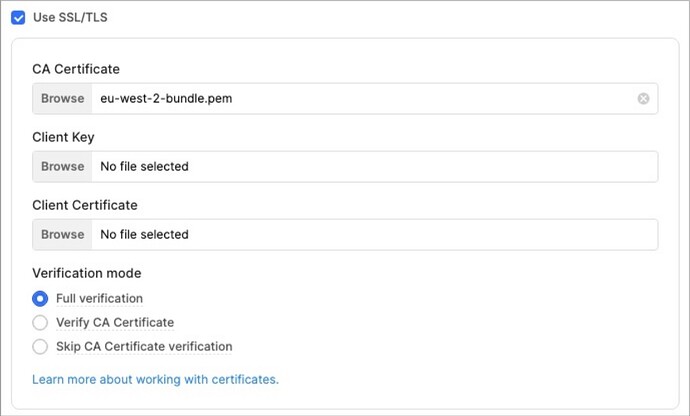
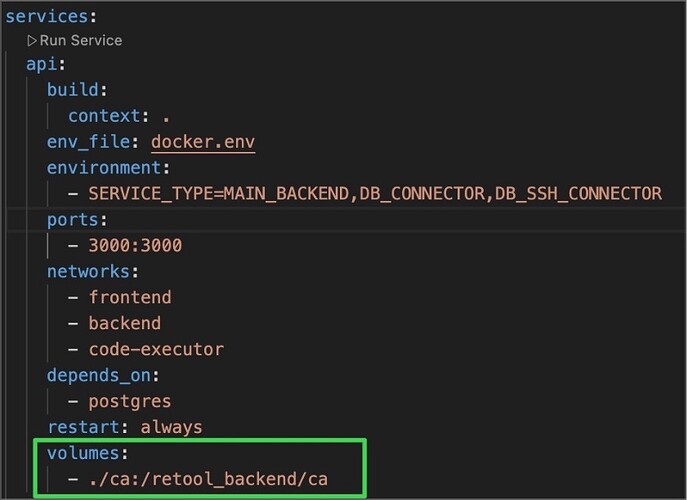
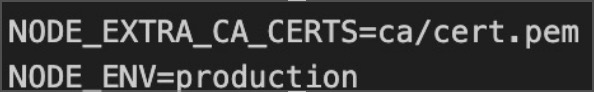
To securely connect Retool to resources protected by custom SSL certificates, you'll need to add your CA certificates to Retool's trusted certificate store.
SSL/TLS is a security technology that protects data as it moves between computers over the internet. These protocols use PEM certificates to verify identity and encrypt communications.This means that when Retool talks to a database or API, SSL ensures it’s talking to the real server and that no one can snoop on the conversation.
When setting up a resource on Retool you might have a username & password authentication set up, for instance. That will protect the resource’s data and ensure that only permitted users can access this data.
-
However, these credentials only control access—they don't encrypt the communication channel itself. Without encryption, anyone intercepting the network traffic between Retool and your resource can view all transmitted data in plain text
-
Without SSL Retool has no way to verify it is connecting to the actual resource server. An attacker could impersonate the resource server and intercept all data sent from Retool, including authentication credentials
SSL certificates address both of these security concerns: they verify the server's identity and encrypt all communication between Retool and your resources:
How SSL Works Between Retool and Databases/APIs
Typical Database SSL/TLS Flow
-
Retool is the client, the resource (DB/API) is the server
-
The server presents its certificate (PEM format) to Retool
-
Retool checks if the certificate is valid and trusted
-
If valid, an encrypted connection is established by Retool and the resource
This may seem counterintuitive—you might expect the server to check the client's certificate to ensure it can be trusted- this is, however, taken care of with the resource authentication (ie. username and password). With SSL connections the client verifies the server's certificate.
Think of it like going to the bank - before you hand over your credit card details, you need to verify you're at the real bank and not a fake storefront run by scammers.
This process ensures the client can be certain it's communicating with the legitimate server and not an impostor. This is called server authentication and protects against man-in-the-middle attacks where attackers impersonate your database or API.
Why Encryption & Verification Matter
Even when the database is in AWS, the connection usually travels across the public internet. Without SSL/TLS, attackers could intercept or impersonate your server—stealing data, credentials, or queries. With SSL/TLS, all data is encrypted, and the client refuses to connect if the server’s identity cannot be verified.
How Retool and Node.js Handle Certificates
When Retool connects to an HTTPS API or cloud database, it's Node.js running inside a Docker container making those network connections. For connections to succeed, Node.js must trust any certificate the server provides.
-
Public CA certificates are trusted by default
-
For internal systems using your own CA, Node.js needs to explicitly be told about your CA
[continued in next post]